|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
Neuro-ophthalmology Quiz 5
|
Printer Friendly
|


Howard Pomeranz, M.D. | Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, Harvard Medical School, University of Maryland Medical Center M.A. Afshari, M.D., M.P.H. | Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, Harvard Medical School August 1, 1997
|
|
[View Answers] [Back to Neuro-ophthalmology]
|
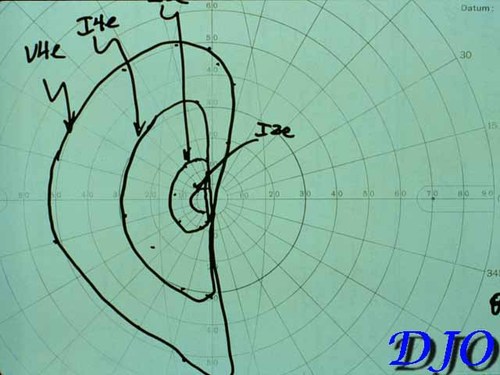
Figure 1
Kinetic Visual Field
|
|
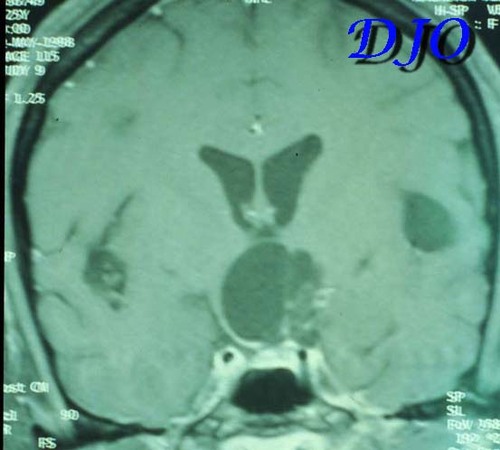
Figure 3
|
| | Case History | A 25 year-old right handed Ecuadorian woman was well until age 20 when she developed seizures. A CT scan of the head revealed calcified cysts in the cerebral cortex. She was treated with tegretol. Twelve months ago she noted the onset of visual loss in her peripheral visual field of the left eye. This visual loss progressed to loss of central vision in the left eye. Two months ago she began to notice loss of peripheral vision in the right eye.
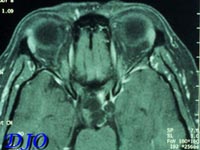
On ophthalmic examination her visual acuity with correction was 20/40 OD and 20/80 OS with no improvement with pinhole. Her color vision was normal bilaterally. There was no evidence of proptosis, ptosis, afferent pupillary defect or ocular motility deficits. Anterior segment exam and intraocular pressures were normal. Kinetic visual field is shown below. Fundus exam revealed myopic optic nerves and temporal pallor of the left optic nerve. A magnetic resonance scan of the head was obtained. Axial and coronal sections are shown below.
References:
Keane, JR. Neuro-ophthalmic signs and symptoms of cysticercosis. Arch Ophthalmol 1982; 100: 1445-1448.
Grisolia JS and Wiederholt WC. CNS cysticercosis. Arch Neurol 1982; 39: 540-544.
McCormick GF, Zee CS and Heiden J. Cysticercosis cerebri: review of 127 cases. Arch Neurol 1982; 39: 534-539.
Odel JG and Moazami G. Diseases caused by helminths. In Walsh and Hoyt's Clinical Neuro-ophthalmology Vol. 4, fifth edition. NR Miller and NJ Newman, eds. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins; 1998: 4460-4479. | | | Questions | 1. What is this patient's most likely diagnosis?
2. What portion of the anterior visual system is most likely affected?
3. What other neuro-ophthalmic problems can arise in patients with this diagnosis?
| | | [View Answers] |
|
 |
 |
 |

|
|
 Welcome, please sign in
Welcome, please sign in  Welcome, please sign in
Welcome, please sign in