Hypopigmentation following briminodine-induced contact dermatitis
Jul 9, 2019
Volume 25, Number 2
Dan Gordon, BS | SUNY Downstate College of Medicine, Brooklyn New York
Anthony Parendo, MD | Department of Ophthalmology, SUNY Downstate Medical Center, Brooklyn, New York
Inci Dersu, MD | Department of Ophthalmology, SUNY Downstate Medical Center, Department of Ophthalmology, Brooklyn, New York
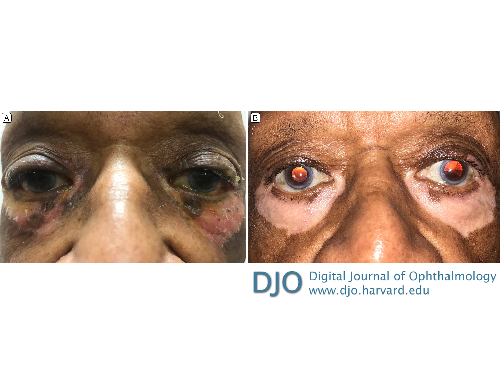
A 92-year-old man with end-stage glaucoma who had previously developed allergic contact dermatitis while using topical brimonidine developed a second episode of dermatitis on rechallenge (A). The inflammation rapidly resolved after discontinuation of brimonidine, but at his next follow-up visit, he complained of new-onset, bilateral periocular depigmentation (B). The patient’s age, lack of any history of autoimmunity, and the localized distribution of his lesions suggested a medication-induced process rather than vitiligo. We believe that this patient’s symptoms are most likely due to post-inflammatory hypopigmentation, a rare but well-documented sequela of allergic contact dermatitis.
 Welcome, please sign in
Welcome, please sign in  Welcome, please sign in
Welcome, please sign in