|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
General Ophthalmology Quiz 8
|
Printer Friendly
|


Yichieh Shiuey, MD | Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, Harvard Medical School February 18, 1998
|
|
[Back to Questions] [Back to General Ophthalmology]
|
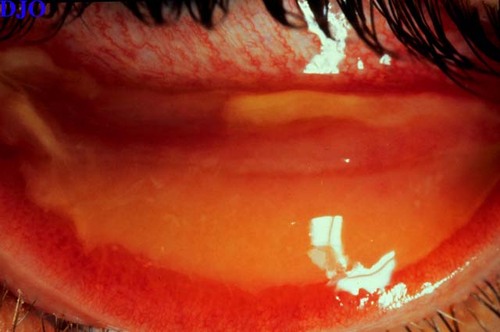
Figure 1
This finding was present on the inferior tarsal conjunctiva of a patient complaining of tearing and redness of his right eye.
|
| Questions and Answers | 1. How can one clinically differenitate between a conjunctival membrane and a conjunctival pseudomembrane?
Answer: Removal of a true membrane is difficult and causes bleeding whereas removal of a pseudomembrane is easy and does not produce bleeding.
2. What is the differential diagnosis of a conjunctival membrane?
Answer: Bacterial conjunctivitis including streptococci, pneumococci, and corynebacterium diphtheria; chemical burns, ligneous conjunctivitis, rarely adenovirus or herpes simplex virus.
3. What is the differential diagnosis of a conjunctival pseudomembrane?
Answer: All of the causes of true membranes; ocular cicatricial pemphigoid, Steven's Johnson syndrome, superior limbic keratoconjunctivitis, gonnococal and chlamydial infection in newborns.
4. What is the most common etiology for this finding?
Answer: Adenovirus (Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis)
5. How would you manage the above finding?
Answer: Determine the underlying cause of the membrane/pseudomembrane and treat the underlying disease. In the case of adenoviral infection removal of the inflammatory membrane and application of topical steroids may prevent the formation of symblepharon.
| | | [Back to Questions] |
|
 |
 |
 |

|
|
 Welcome, please sign in
Welcome, please sign in  Welcome, please sign in
Welcome, please sign in