|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
General Ophthalmology Quiz 3
|
Printer Friendly
|


Yichieh Shiuey, MD | Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, Harvard Medical School May 20, 1997
|
|
[Back to Questions] [Back to General Ophthalmology]
|
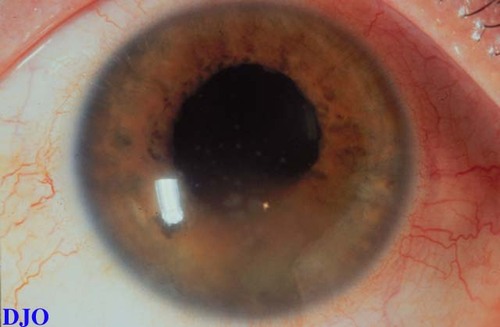
Figure 1
This is a patient who developed increasing photophobia over the course of weeks.
|
| Questions and Answers | 1. What is the clinical finding shown in the photograph?
Answer: Mutton fat keratic precipitates.
2. What is the differential diagnosis for the clinical finding shown?
Answer: Mutton fat keratic precipitates are suggestive of a chronic granulomatous process. The differential diagnosis includes sarcoidosis, syphyllis, and tuberculosis. Other unusual chronic infections may also produce mutton fat keratic precipitates e.g. leprosy, brucellosis, coccidiomycosis.
3. What iris findings may be associated with the above clinical picture?
Answer: Koeppe's nodules ( inflammatory nodules on the pupillary border) and Busacca's nodules (inflammatory nodules on the anterior iris surface) are both associated with chronic granulomatous anterior uveitis. Posterior and anterior synechiae may also be found.
4. What questions regarding the patient's medical history should be asked?
Answer: The possibility of exposure to tuberculosis or syphyllis should be explored. Pulmonary symptoms should be elicited as these are frequently present in both sarcoidosis and tuberculosis. Questions regarding constitutional symptoms such as fever, weight loss, and fatigue should also be asked.
5. What tests should be ordered if the history is unrevealing?
Answer: CBC, ESR, ANA, VDRL, FTA-ABS, PPD and anergy panel, Chest X-ray. An HLA-B27 may also be considered, although HLA-B27 uveitis is more typically non-granulomatous.
| | | [Back to Questions] |
|
 |
 |
 |

|
|
 Welcome, please sign in
Welcome, please sign in  Welcome, please sign in
Welcome, please sign in