|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
A 56-year-old man with a unilateral central scotoma
Digital Journal of Ophthalmology 2021
Volume 27, Number 3
September 27, 2021
|
Printer Friendly
Download PDF |
|
|


Khushali Shah, BA | University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, Miami, Florida; Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, Miami, Florida Benjamin J. Fowler, MD, PhD | Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, Miami, Florida Benjamin Lin, MD | Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, Miami, Florida Kara M. Cavuoto, MD | Bascom Palmer Eye Institute Jayanth Sridhar, MD | Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, Miami, Florida
|
|
|
| Treatment | | The patient was admitted to the hospital for treatment of ocular syphilis. He received 14 days of intravenous penicillin G, dosed at 3,000,000 units every 4 hours. On hospital day 6, the patient endorsed subjective improvement in visual disturbances. On 2-week follow-up, best-corrected visual acuity in the right eye improved to 20/40, with resolution of the scotoma. Repeat OCT showed partial reconstitution of the EZ and reduction in sub-RPE deposits (Figure 3).(1,2) Six weeks after completing treatment, the patient’s best-corrected visual acuity improved to 20/25 in the right eye, and he had mild residual macular RPE pigmentary abnormalities on examination (Figure 4). Fundus autofluorescence (FAF) demonstrated a patchy, speckled hyperautofluorescent pattern in the area previously taken up by the placoid lesion (Figure 5). OCT imaging after 6 weeks revealed complete resolution of sub-RPE deposits (Figure 6). | |
|
Figure 3.
SD-OCT on 2-week follow-up after treatment showing partial reconstitution of EZ and reduction in sub-RPE deposits.
 |
|
|
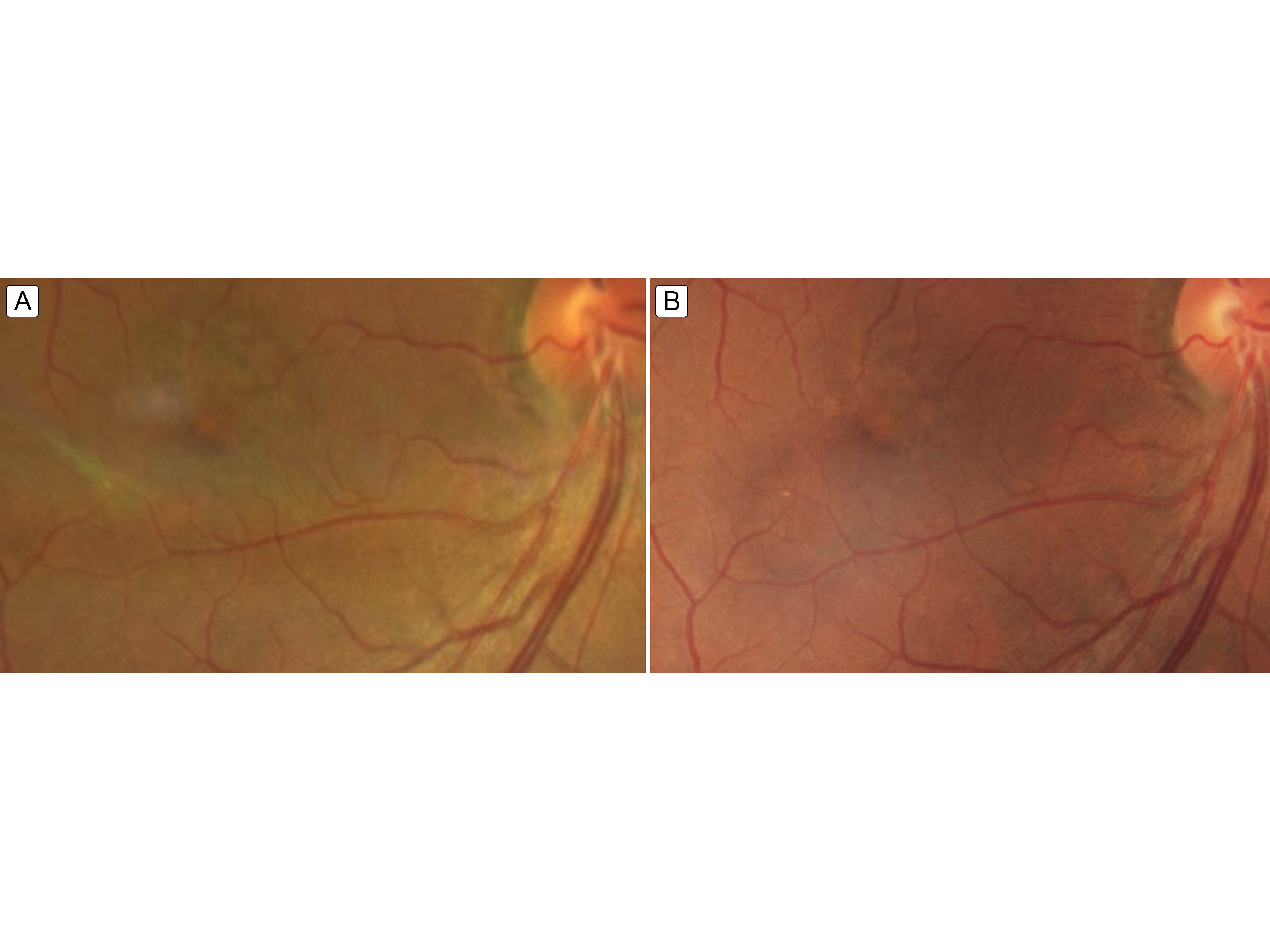
Figure 4.
Fundus image 2 weeks (A) and 6 weeks (B) after completing intravenous penicillin treatment showing ongoing but resolving mild foveal pigment mottling.
 |
|
|
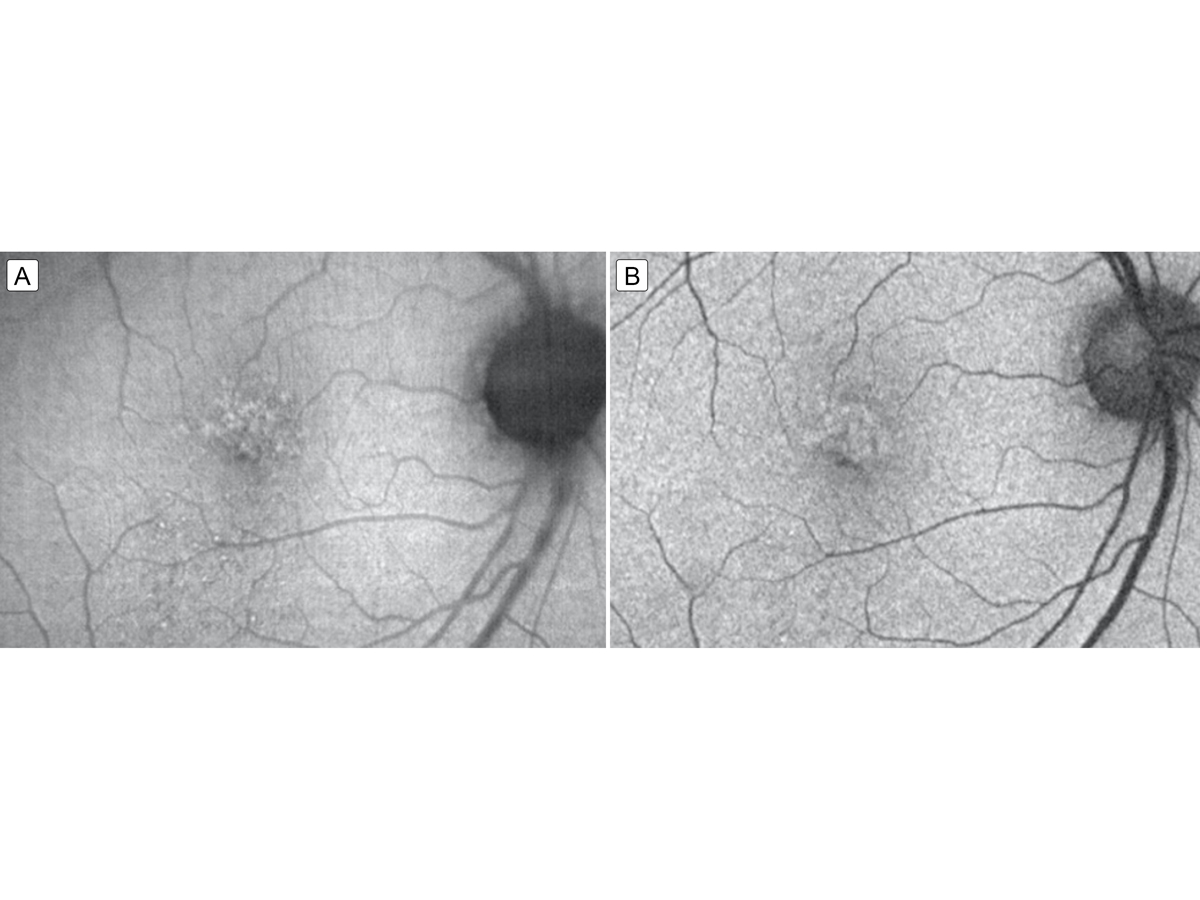
Figure 5.
Fundus autofluorescence 2 weeks (A) and 6 weeks (B) after completing intravenous penicillin treatment showing resolving punctate hyperfluorescent lesions that correspond to the resolving placoid lesion.
 |
|
|
Figure 6.
SD-OCT on 6-week follow up with resolution of sub-RPE deposits and mild residual sub-foveal disruption of photoreceptor outer segments.
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |

|
|
 Welcome, please sign in
Welcome, please sign in  Welcome, please sign in
Welcome, please sign in