|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
Bilateral uveal effusions in a 23-year-old man
Digital Journal of Ophthalmology 2018
Volume 24, Number 2
May 22, 2018
DOI: 10.5693/djo.03.2018.03.001
|
Printer Friendly
|
|
|


Karen W. Jeng-Miller, MD, MPH | Department of Ophthalmology, Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts Eric D. Gaier, MD, PhD | Department of Ophthalmology, Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts Angela V. Turalba, MD | Department of Ophthalmology, Atrius Health, Boston, Massachusetts
|
|
|
| Ancillary Testing | | Biometry testing revealed an axial length of 22.43 mm in the right eye and 22.26 mm in the left eye as measured by LENSTAR LS 900 Biometer (Haag-Streit USA). His anterior chamber depth was recorded at 2.06 mm in the right eye and 2.03 mm in the left eye. B-scan ultrasonography revealed uveal effusions without ocular masses (Figure 1) and ultrasound biomicroscopy (UBM) confirmed shallow anterior chambers with uveal effusions in both eyes (Figure 2A). | |
|
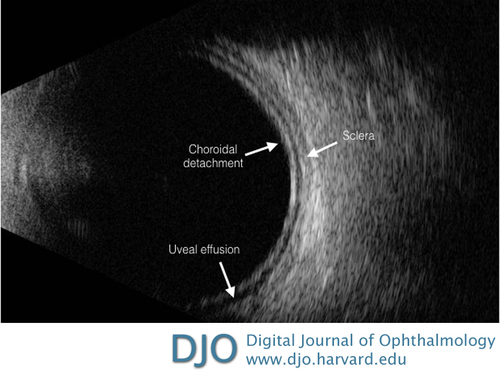
Figure 1
B-scan ultrasound of the left eye showing uveal effusion and no evidence of an intraocular mass. The same findings were present in the right eye.
 |
|
|
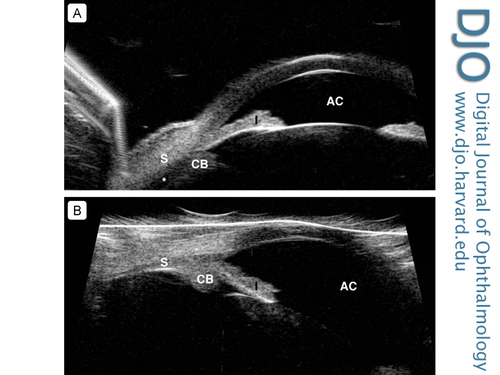
Figure 2
A, Ultrasound biomicroscopy (UBM) of the left eye showing evidence of peripheral uveal effusion (asterisk) and shallow anterior chamber (AC). The same findings were present in the right eye. B, UBM of the left eye demonstrating resolution of the peripheral uveal effusions with deepening of the anterior chamber. CB, ciliary body; I, iris; S, sclera.
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |

|
|
 Welcome, please sign in
Welcome, please sign in  Welcome, please sign in
Welcome, please sign in