Glaucoma Quiz 6

Figure 1
Correctopia and full thickness iris defects.
Correctopia and full thickness iris defects.

Figure 2
Gonioscopic view.
Broad leaves of iris stroma adherent to the cornea anterior to Schwalbe's line. Angle architecture is poorly differentiated.
Gonioscopic view.
Broad leaves of iris stroma adherent to the cornea anterior to Schwalbe's line. Angle architecture is poorly differentiated.
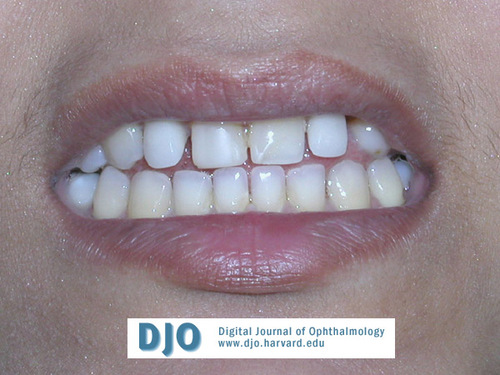
Figure 3
Teeth.
Microdontia.
Teeth.
Microdontia.

Figure 4
Umbilicus
Post surgical changes noted after removal of redundant skin.
Umbilicus
Post surgical changes noted after removal of redundant skin.
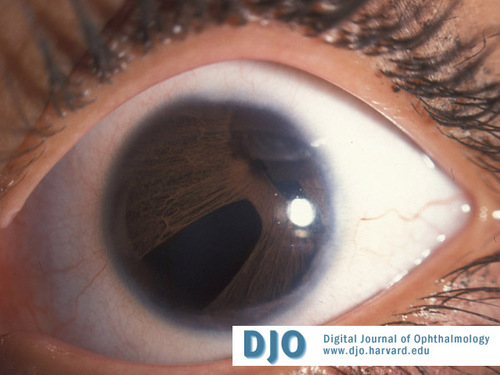
Left eye
Correctopia and full thickness iris defects.
Correctopia and full thickness iris defects.

Gonioscopic view
Broad leaves of iris stroma adherent to the cornea anterior to Schwalbe's line. Angle architecture is poorly differentiated.
Broad leaves of iris stroma adherent to the cornea anterior to Schwalbe's line. Angle architecture is poorly differentiated.
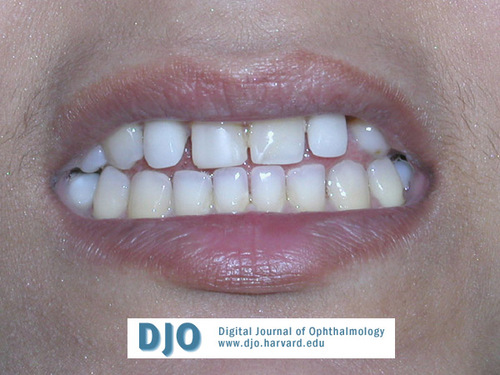
Teeth
Microdontia.
Microdontia.
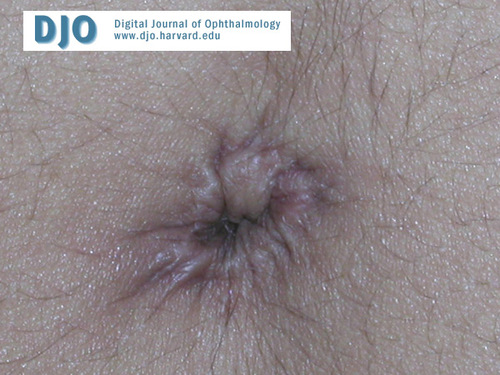
Umbilicus
Post surgical changes noted after removal of redundant skin.
Post surgical changes noted after removal of redundant skin.
Answer: Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome. Anterior segment dysgenesis constitutes a spectrum of maldevelopment of the anterior segment, including the cornea, iris and angle. A prominent, axially displaced Schwalbe's line is known as posterior embryotoxin. Prominent iris processes attached to Schwalbe’s line is Axenfeld’s anomaly. Axenfeld’s syndrome is associated with glaucoma and possible extraocular malformations. Axenfeld’s anomaly and anterior stromal hypoplasia of the iris is Rieger’s anomaly. Glaucoma is seen in up to 60% of these patients. In Rieger’s syndrome, extraocular abnormalities are also seen.
2. What is the inheritance pattern?
Answer: Usually autosomal dominant (75%), but may be sporadic.
3. What is the main associated ocular condition?
Answer: Glaucoma in Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome is more refractory to medical therapy than open angle glaucoma and may require aggressive therapy. Gonioscopic evaluation is mandatory.
4. What extraocular anomalies may be seen?
Answer: Dental (hypodontia, microdontia); facial (maxillary hypoplasia, broad nasal bridge, telecanthus, hypertelorism); others (redundant periumbilical skin, defects in region of pituitary gland).