Pathology Quiz 7
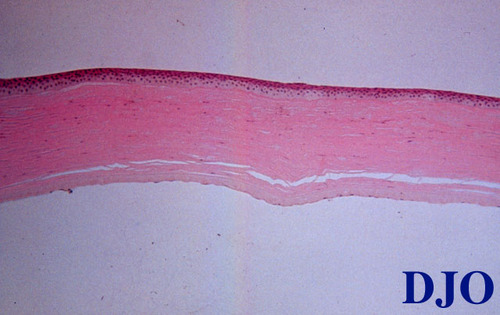
Figure 1
Figures 1-2. Corneal histopathology, Periodic-acid Schiff stain.
Figures 1-2. Corneal histopathology, Periodic-acid Schiff stain.
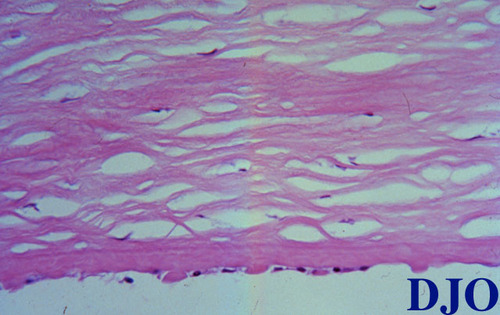
Figure 2
Answer: Primary Endothelial Degeneration (Fuchs' corneal dystrophy).
2. What are the histologic characteristics of the lesion?
Answer: In Fuchs' corneal dystrophy, the epithelium and stroma are frequently edematous. There may be bullae and subepithelial fibrous scar present. The Descemet's membrane is often thickened with characteristic guttata seen on PAS stain. The endothelium is attenuated.
3. What is the most appropriate treatment for this lesion?
Answer: No treatment is needed for asymptomatic patients. However, in the later stages of the disease, treatment may be needed for the complications, such as epithelial edema causing decreased vision and for pain secondary to ruptured bullae. Non-surgical treatments for epithelial edema include use of hypertonic drops and ointment (e.g. NaCl 5%) or rarely the use of a hair dryer held at arm's length to dehydrate the cornea. Penetrating keratoplasty is the surgical treatment for cases which fail medical management.
4. What is the inheritance pattern of this condition?
Answer: Autosomal dominant.