Neuro-ophthalmology Quiz 3

Figure 1
Figures 1-2. Fundus photographs of an obese 19 year old woman with headache.
Figures 1-2. Fundus photographs of an obese 19 year old woman with headache.
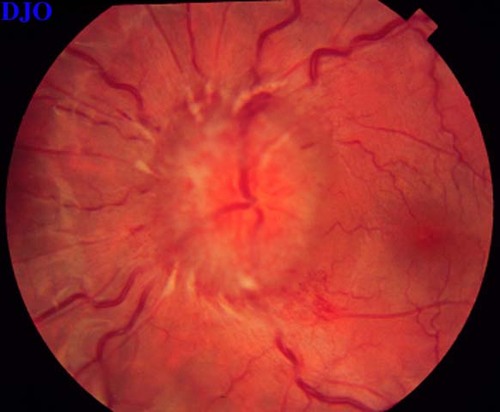
Figure 2
Answer: Bilateral disc edema.
2. What is the most likely etiology for this condition?
Answer: Increased intracranial pressure.
3. What are you likely to find on visual field testing?
Answer: An enlarged blind spot in both eyes, which corresponds to the papilledema. Other visual field defects may also be present, particularly in the inferonasal quadrant.
4. What study should be done next and why?
Answer: An MRI or CT of the brain, to evaluate potential causes of elevated intracranial pressure, especially tumor.
5. This study was completely normal, what should be done next and why?
Answer: A lumbar puncture, to evaluate the CSF composition and measure the opening pressure. The opening pressure in this patient was 450mm of water, and the CSF composition was normal.
6. Given the results of the previous studies what is the most likely diagnosis?
Answer: Pseudotumor cerebri.
7. How would you treat this patient?
Answer: Treatment begins with weight loss and careful observation with serial visual field examinations. Oral acetazolamide may be used to decrease CSF production and lower intracranial pressure.
8. If maximum medical therapy failed and there was progressive visual field or acuity loss what would be your next step?
Answer: Optic nerve sheath fenestration of the more severely affected eye. This may also relieve the edema of the contralateral optic disc.