General Ophthalmology Quiz 2
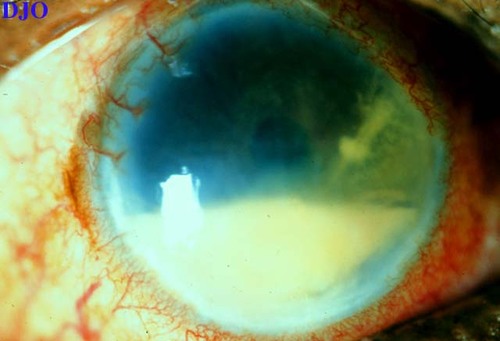
Figure 1
This is a patient who underwent cataract surgery 10 days earlier who has noticed progressive worsening of vision and mild pain in this eye.
This is a patient who underwent cataract surgery 10 days earlier who has noticed progressive worsening of vision and mild pain in this eye.
Answer: Postoperative bacterial endophthalmitis is the most likely diagnosis with this clinical picture. Other conditions to consider would be sterile post-surgical inflammation, inflammation FROM retained lens material, flare of uveitis, and endogenous endophthalmitis
2. If aqueous and vitreous cultures were taken, what organism(s) would be most likely to be found?
Answer: Staphylococcus epidermidis is the most common pathogen overall in post-operative endophthalmitis and usually has a subacute course, presenting within the first 14 days with mild to moderate pain and vision typically better than 20/400. More aggressive pathogens include Staphlyococcus aureus, Streptococcus species, and gram negative bacteria. These bacteria usually present clinically with more severe visual loss (i.e. worse than 20/400) and more pain as well as a more rapid onset. Endophthalmitis occurring longer than 14 days after surgery may be caused by S. epidermidis, Propionibacterium acnes, and fungus.
3. What can be done pre-operatively to prevent the above condition?
Answer: Pre-operative topical antibiotics and 5% povidone-iodine instilled INTO the conjunctival fornices have been shown to decrease bacterial colony counts. Careful draping of the eyelids and eye-lashes is important to prevent contamination of the surgical field. Post-operative subconjunctival injections of antibiotics are of unproven benefit.
4. If aqeuous and vitreous samples were taken, for which laboratory tests should these samples be sent for?
Answer: Immediate Gram stain for bacteria and Giemsa for fungus (if fungus is suspected), since if the stain is positive, this will give guidance on initial empiric therapy. The aqueous and vitreous samples must also be sent for culture. The samples should be inoculated directly onto culture media including: blood agar (aerobic and anaerobic), Saboraud's agar, chocolate agar, and thioglycolate broth. If P. acnes is suspected, anaerobic cultures should be held at least 2 weeks because the organism is slow growing.
5. How should you treat this patient?
Answer: The endophthalmitis vitrectomy study suggests that intravitreal injection of broad-spectrum antibiotics alone without vitrectomy or intravenous antibiotics may be sufficient for many patients with post-operative endophthalmitis. Vitrectomy and intravenous broad spectrum antibiotics may be indicated in some patients with severe infectious post-operative endophthalmitis.